717 Newfield St. Middletown, CT 06457


Last Updated: May 13, 2025
Medically Reviewed By:
Dr. John Pavlakis, Cosmetic Dentist
Do you notice pink in the sink when you brush your teeth? This common symptom might indicate gum disease, a condition that affects nearly half of American adults. Recognizing the early signs of gum disease can help you seek treatment before it progresses to more serious stages.
At Advanced Family & Cosmetic Dentistry, we help patients identify and treat gum disease at all stages. Our comprehensive approach focuses on both resolving current symptoms and preventing future occurrences, ensuring your smile remains healthy and beautiful for years to come.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that surround and support your teeth. It begins with bacterial growth in your mouth and, if not properly treated, can lead to tooth loss due to the destruction of the tissue that surrounds your teeth.
The disease typically progresses through two main stages. Gingivitis, the milder and reversible form, causes inflammation of the gums but doesn’t affect the bone or supporting tissues. Left untreated, gingivitis can advance to periodontitis, where the inner layer of the gum and bone pull away from the teeth and form pockets that collect debris and become infected.
Bacteria in plaque, a sticky film that constantly forms on teeth, is the primary cause of gum disease. However, other factors can increase your risk, including smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, genetic susceptibility, and systemic diseases like diabetes.
Early Warning Signs of Gum Disease
Catching gum disease in its early stages offers the best chance for successful treatment with minimal intervention. Watch for these warning signs:
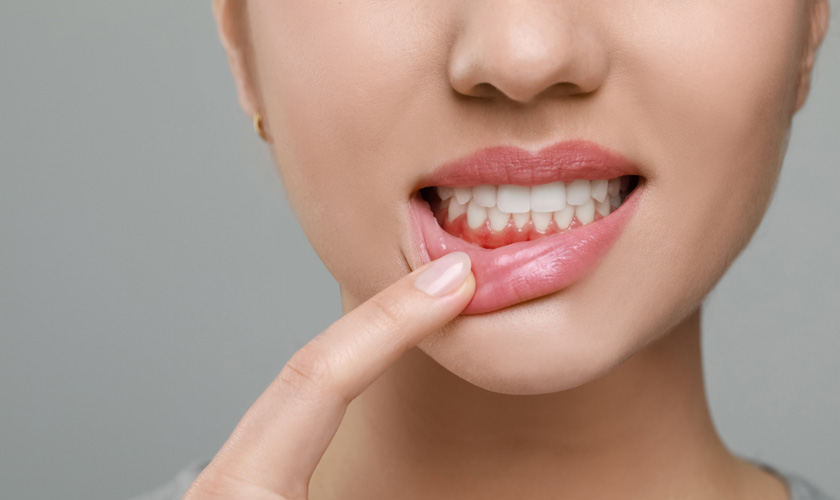
Bleeding Gums
One of the most common early indicators of gum disease is bleeding during brushing or flossing. Healthy gums should not bleed during routine oral care. If you notice blood in the sink after brushing, this suggests inflammation and requires attention.
Many people mistakenly believe bleeding gums are normal or simply the result of brushing too hard. While aggressive brushing can cause bleeding, consistent bleeding, even with gentle brushing techniques, strongly indicates gum inflammation.
Persistent Bad Breath
Chronic bad breath that doesn’t improve with brushing, flossing, or mouthwash can signal the presence of bacteria causing gum disease. The bacteria release sulfur compounds that create an unpleasant odor.
Unlike temporary bad breath from food, gum disease-related halitosis persists throughout the day because the source – bacteria in the gum pockets – remains present. If your bad breath continues despite good oral hygiene, it’s time to consult a dental professional.
Red, Swollen, or Tender Gums
Healthy gums appear firm and pink, fitting snugly around teeth. Inflamed gums look red, puffy, and may feel tender to the touch. This inflammation results from your body’s immune response to bacterial invasion.
The change in color and texture can be subtle at first, making it easy to overlook. Regular visual inspection of your gums in a mirror can help you notice these changes early.
Advanced Signs That Require Immediate Attention
As gum disease progresses, more serious symptoms develop that indicate advancing periodontitis. These signs warrant prompt, professional care:
Receding Gums
When gums pull away from teeth, they create pockets where bacteria can accumulate. This recession makes teeth appear longer and creates spaces between teeth where food can become trapped.
Gum recession occurs gradually, often without pain, making it difficult to notice day-to-day changes. Comparing current photos of your smile to older ones can sometimes reveal this progression.
Loose or Shifting Teeth
As periodontitis advances, the supporting structures of your teeth, including bone, begin to deteriorate. This deterioration can cause teeth to become loose or shift position, affecting your bite and the way your teeth fit together.
You might notice changes when chewing or speaking, or realize that gaps are developing between previously tight teeth. These changes indicate significant progression of the disease and require immediate professional intervention.
Persistent Pus Between Teeth and Gums
Pus discharge around the gumline indicates active infection. You might notice white or yellow fluid when pressing on the gums, or taste a persistent metallic flavor in your mouth.
This symptom represents an advanced infection that your body is actively fighting. Professional treatment is essential to eliminate the infection and prevent further damage to oral tissues.
How Dentists Diagnose Gum Disease
When you visit Advanced Family & Cosmetic Dentistry with concerns about gum disease, we conduct a thorough assessment to determine the presence and severity of the condition.
Our diagnostic process typically includes:
- Reviewing your medical history and risk factors
- Examining your gums for inflammation, pockets, and recession
- Measuring the depth of any gum pockets using a special probe
- Taking dental X-rays to check for bone loss around the teeth
- Assessing tooth mobility and bite changes
This comprehensive evaluation helps us determine the stage of gum disease and develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Professional Treatments for Gum Disease
Treatment options vary based on the severity of your gum disease. Our approach focuses on controlling the infection, removing factors that contribute to disease progression, and restoring supportive tissues when possible.
Non-Surgical Treatments
For early to moderate gum disease, non-surgical approaches can be very effective:
Scaling and Root Planing
This deep-cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line (scaling) and smooths the tooth roots (planing) to help gums reattach to teeth. The treatment may require multiple visits and is performed with local anesthesia to ensure your comfort.
Scaling and root planing can significantly reduce pocket depths and inflammation when performed by skilled dental professionals. This procedure often serves as the first line of treatment for periodontitis.
Antibiotic Therapy
In some cases, we may recommend topical or oral antibiotics to control bacterial infection. These medications complement mechanical cleaning procedures by targeting bacteria in areas difficult to reach with instruments alone.
Antibiotic treatments may include mouth rinses, gels applied directly to the gum pockets, or oral medications. These approaches help reduce bacterial counts and control inflammation while your tissues heal.
Surgical Treatments for Advanced Cases
When gum disease has progressed significantly, surgical interventions may be necessary:
Flap Surgery
For deep pockets that persist after non-surgical treatments, flap surgery allows for a more thorough cleaning of the roots and can reduce pocket depth. During this procedure, the gums are temporarily lifted to provide better access to roots and bone.
After cleaning, the gums are sutured back into place to fit snugly around the teeth. This procedure helps create an environment that’s easier to keep clean with daily oral hygiene.
Bone and Tissue Grafts
When periodontitis has destroyed bone or gum tissue, grafting procedures can help regenerate these lost structures. Bone grafts use natural or synthetic bone to stimulate new bone growth, while soft tissue grafts address significant gum recession.
These regenerative procedures can help stabilize teeth, improve appearance, and enhance long-term prognosis. Recovery typically takes several weeks, but the benefits continue as new tissue integrates and strengthens.
Preventing Gum Disease Recurrence
After successful treatment, maintaining good oral health becomes crucial to prevent recurrence. We recommend:
- Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Flossing daily to remove plaque between teeth
- Using antimicrobial mouth rinses as recommended
- Quitting tobacco use, which significantly increases gum disease risk
- Managing conditions like diabetes that can impact gum health
- Scheduling regular professional cleanings and check-ups
The frequency of maintenance visits depends on your individual risk factors and history, but most patients benefit from professional cleanings every three to six months after gum disease treatment.
Contact Advanced Family & Cosmetic Dentistry Today
At Advanced Family & Cosmetic Dentistry, we’re committed to helping patients achieve and maintain optimal gum health through personalized care and education. Our team uses advanced techniques to diagnose and treat periodontal disease at all stages. As a non-restricted provider, we focus on patient-centered treatment planning that prioritizes your health and aesthetic goals over insurance limitations while still submitting insurance claims to maximize your reimbursement.
We understand that gum disease can be concerning, but with proper care and maintenance, most patients can successfully manage this condition and preserve their natural teeth. If you’re noticing any signs of gum disease or are due for a dental check-up, call us at (860) 347-1227 or visit our contact form.